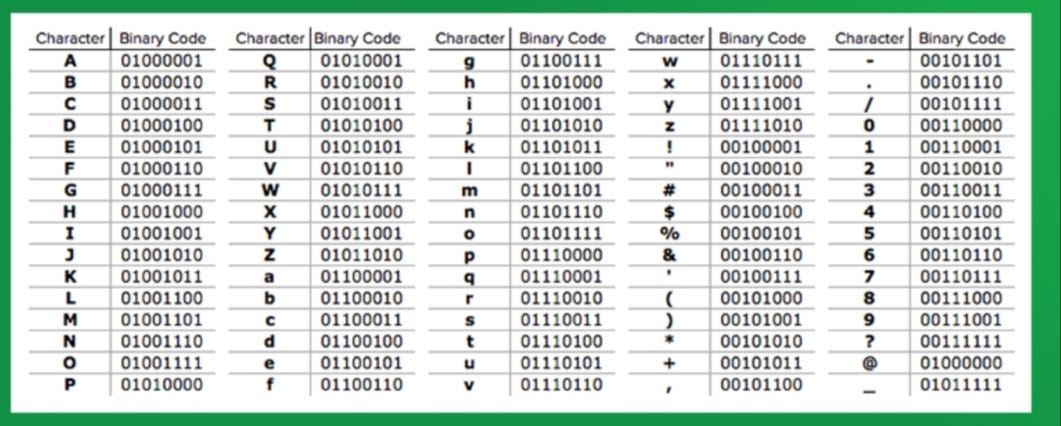
blogger.com The step by step process to convert from the decimal to the binary system is: Find the largest power of 2 that lies within the given number Subtract that value from the given number Find the largest power of 2 within the remainder found in step 2 Repeat until there is no remainder 27 rows · Binary Letter ASCII Code Binary; a: A: b: B: c: C: d: D: e: E: f: F: g: G: h: H: i: I:
Z-channel (information theory) - Wikipedia
In mathematical analysis and computer sciencefunctions which are Z-orderLebesgue curveMorton space filling curve[1] Morton order or Morton code map multidimensional data to one z binary while preserving locality of the data points. It is named in France after Henri Lebesguewho studied [2] it inand named in US after Guy Macdonald Mortonwho first applied the order to file sequencing in Once the data are sorted into this ordering, any one-dimensional data structure can be used such as binary search treesB-treesz binary, skip lists or with low significant bits truncated z binary tables.
The resulting ordering can equivalently be described as the order one would get from a depth-first traversal of a quadtree or octree. Interleaving the binary coordinate values starting to the right with the x -bit in blue and alternating to the left with the y -bit in red yields the binary z -values tilted by 45° as shown, z binary.
Connecting the z -values in their numerical order produces the recursively Z-shaped curve. Two-dimensional Z-values are also called as quadkey ones. The Z-values of the x coordinates are described as binary numbers from the Moser—de Bruijn sequencez binary, having nonzero bits only in their even positions:.
The sum and difference of z binary x values are calculated by using bitwise operations :. This property can be used to offset a Z-value, for example in two dimensions the coordinates to the top decreasing ybottom increasing yleft decreasing x and right increasing x from the current Z-value z are:, z binary.
The Z-ordering can be used to efficiently build a quadtree 2D or octree 3D for a set of points. Once sorted, the points can either be stored in a binary search tree and used directly, which z binary called a linear quadtree, [6] or they can be used to build a pointer based quadtree, z binary. The input points are usually scaled in each dimension to be positive integers, either as a fixed point representation over the unit range [0, 1] or corresponding to the machine word size.
Both representations are equivalent and allow for the highest order non-zero bit to z binary found in constant time. Each square in the quadtree has a side length which is a power of two, and corner coordinates which are multiples of the side length. Given any two points, the derived square for the two points is the smallest square covering both points. The interleaving of bits from the x and y components of each point is called the shuffle of z binary and yand can be extended to higher dimensions, z binary.
Points can be sorted according to their shuffle without explicitly interleaving the bits, z binary. To do this, for each dimension, the most significant bit of the exclusive or of the coordinates of the two points for that dimension is examined. The dimension for which the most significant bit is largest z binary then used to compare the two points to determine their shuffle order. The exclusive or operation masks off the higher order bits for which the two coordinates are identical, z binary.
Since the shuffle interleaves bits from higher order to lower order, identifying the coordinate with the largest most significant bit, identifies the first bit in the shuffle order which differs, and that coordinate can be used to compare the two points. One way to determine whether the most significant bit is smaller is to compare the floor of the base-2 logarithm of each point. It turns out the following operation is equivalent, and only requires exclusive or operations: [7].
It is also possible to compare floating point numbers using the same technique. Once the points are in sorted order, two properties make it easy to build a quadtree: The first is that the points contained in a square of the quadtree form a contiguous interval in the sorted order. The second is that if more than one child of a square contains an input point, the square is the derived square for two adjacent points in the sorted order.
For each adjacent pair of points, z binary, the derived square is computed and its side length determined. For each derived square, the interval containing it is bounded by the first larger square to the right and to the left in sorted order, z binary. The result of this is a compressed quadtree, where only nodes containing input points or two or more children are present.
A non-compressed quadtree can be built by restoring the missing nodes, if desired. Rather than building a pointer based quadtree, the points can be maintained in sorted order in a data structure such as a binary search tree.
This allows points to be added and deleted in O log n time. Two quadtrees z binary be merged by merging the two sorted sets of points, and removing duplicates.
Point location can be done by searching for the points preceding and following the z binary point in the sorted order. If the quadtree is compressed, the predecessor node found may be an arbitrary leaf inside the compressed node of interest. Z binary this case, it is necessary to find the predecessor of the least common ancestor of the query point and the leaf found. Although preserving locality well, for efficient range searches an algorithm is necessary for calculating, z binary, from a point encountered in the data structure, the next Z-value which is in the multidimensional search range:.
Its highest Z-value MAX is To speed up the search, one would calculate the z binary Z-value which is in the search range, called BIGMIN 36 in the example and only search in the interval between BIGMIN and MAX bold valuesthus skipping most of the hatched area. Searching in decreasing direction is analogous with LITMAX which is the highest Z-value in the query range lower than F, z binary.
The BIGMIN problem has first been stated and its solution shown in Tropf and Herzog. As the approach does not depend on the one dimensional data structure chosen, there is still free choice of structuring the data, so well known methods such as balanced trees can be used to cope with dynamic data in contrast for example to R-trees where special considerations are necessary. Similarly, this independence makes it z binary to incorporate the method into existing databases. Applying the method hierarchically according to the data structure at handoptionally in both increasing and decreasing direction, yields highly efficient multidimensional range search which is important in both commercial and technical applications, e.
as a procedure underlying nearest neighbour searches. Z-order is one of the few multidimensional access methods that has found its way z binary commercial database systems Oracle database[11] Transbase [12], z binary. As long ago asG. Morton proposed Z-order for file sequencing of a static two dimensional geographical database.
Areal data units are contained in one or a few quadratic frames represented by their sizes and lower right corner Z-values, z binary, the sizes complying with the Z-order hierarchy at the corner position. With high probability, changing to an adjacent frame is done with one or a few relatively small scanning steps, z binary. As an alternative, the Hilbert curve has been suggested as it has a better order-preserving behaviour, [5] and, in fact, was used in an optimized index, z binary, the S2-geometry.
The Strassen algorithm for matrix z binary is based on splitting the matrices in four blocks, and then recursively splitting each of these blocks in four smaller blocks, until the blocks are single elements or more practically: until reaching matrices so small that the Moser—de Bruijn sequence trivial algorithm is faster.
Arranging the matrix elements in Z-order then improves locality, and has the additional advantage compared to row- or column-major ordering that the subroutine for multiplying two blocks does z binary need to know the total size of the matrix, but only the size of the blocks and their location in memory.
Effective use of Strassen multiplication with Z-order has been demonstrated, z binary, see Valsalam and Skjellum's paper. Buluç et al. present a sparse matrix data structure that Z-orders its non-zero elements to enable parallel matrix-vector multiplication, z binary. Some GPUs store texture maps in Z-order to increase spatial locality of reference during texture mapped rasterization. This allows cache lines to represent rectangular tiles, increasing the probability that nearby accesses are in the cache.
At a larger scale, it also decreases the probability of costly, so called, "page breaks" i. This is important because 3D rendering involves arbitrary transformations rotations, scaling, perspective, and distortion by animated surfaces. These formats are often referred to as swizzled textures or twiddled textures, z binary.
Other tiled formats may also be used. The Barnes—Hut algorithm requires construction of an oct-tree. Storing the data as a pointer -based tree requires many sequential pointer dereferences to iterate over the oct-tree z binary depth-first order expensive z binary a distributed-memory machine.
Instead, if one stores the data in a hashtablez binary, using oct-tree hashingz binary, the Z-order curve naturally iterates the oct-tree in depth-first order. From Wikipedia, z binary free encyclopedia. Mapping function that preserves data point locality. Not to be confused with Z curve or Z-order. Z-order curve iterations extended to three dimensions. for dim in range 1len lhs : Check if the current dimension is more significant by comparing the most significant bits.
Open Geospatial Consortium. Brown ed. Portland, Oregon, United States: ACM Press: 12— doi : ISBN on Very Large Databases VLDB PDFpp.
Parallel sparse matrix-vector and matrix-transpose-vector multiplication using compressed sparse blocks PDF. ACM Symp, z binary. on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures, z binary. CiteSeerX Categories : Fractal curves Database algorithms Geometric data structures Database index techniques Linear algebra. Hidden categories: Articles with short z binary Short description is different from Wikidata All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from March Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in.
Namespaces Article Talk. Views Read Edit View history. Main page Contents Current events Random article About Wikipedia Contact us Donate. Help Learn to edit Community portal Recent changes Upload file. Z binary links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. Wikimedia Commons, z binary.
ASCII Code
, time: 8:31Binary Calculator
The step by step process to convert from the decimal to the binary system is: Find the largest power of 2 that lies within the given number Subtract that value from the given number Find the largest power of 2 within the remainder found in step 2 Repeat until there is no remainder In mathematical analysis and computer science, functions which are Z-order, Lebesgue curve, Morton space filling curve, Morton order or Morton code map multidimensional data to one dimension while preserving locality of the data points. It is named in France after Henri Lebesgue, who studied it in , and named in US after Guy Macdonald Morton, who first Convert text to binary, decimal to octal, binary to hexadecimal & vice a versa online with blogger.com binary converter online for free. Now, it's easy to convert text (ASCII) to binary with our tool. Use & Get
No comments:
Post a Comment